The Ultimate Quality of Earnings (QoE) Checklist: Your Guide to Financial Due Diligence
Estimated Reading Time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Understand the importance of a Quality of Earnings (QoE) report in financial due diligence.
- Differentiate between QoE reports and traditional audits.
- Utilize a comprehensive QoE checklist to assess financial health.
- Explore key components of QoE reports, including EBITDA normalization.
- Implement AI-enabled solutions to optimize financial processes.
Table of Contents
Understanding Quality of Earnings (QoE)
What is a QoE Report?
A Quality of Earnings (QoE) report is an independent, third-party analysis of a company’s financial records. Its primary purpose is to verify the sustainability and accuracy of reported earnings by:
- Adjusting for non-recurring items
- Scrutinizing financial projections
- Assessing revenue recognition practices
- Evaluating accounting policies
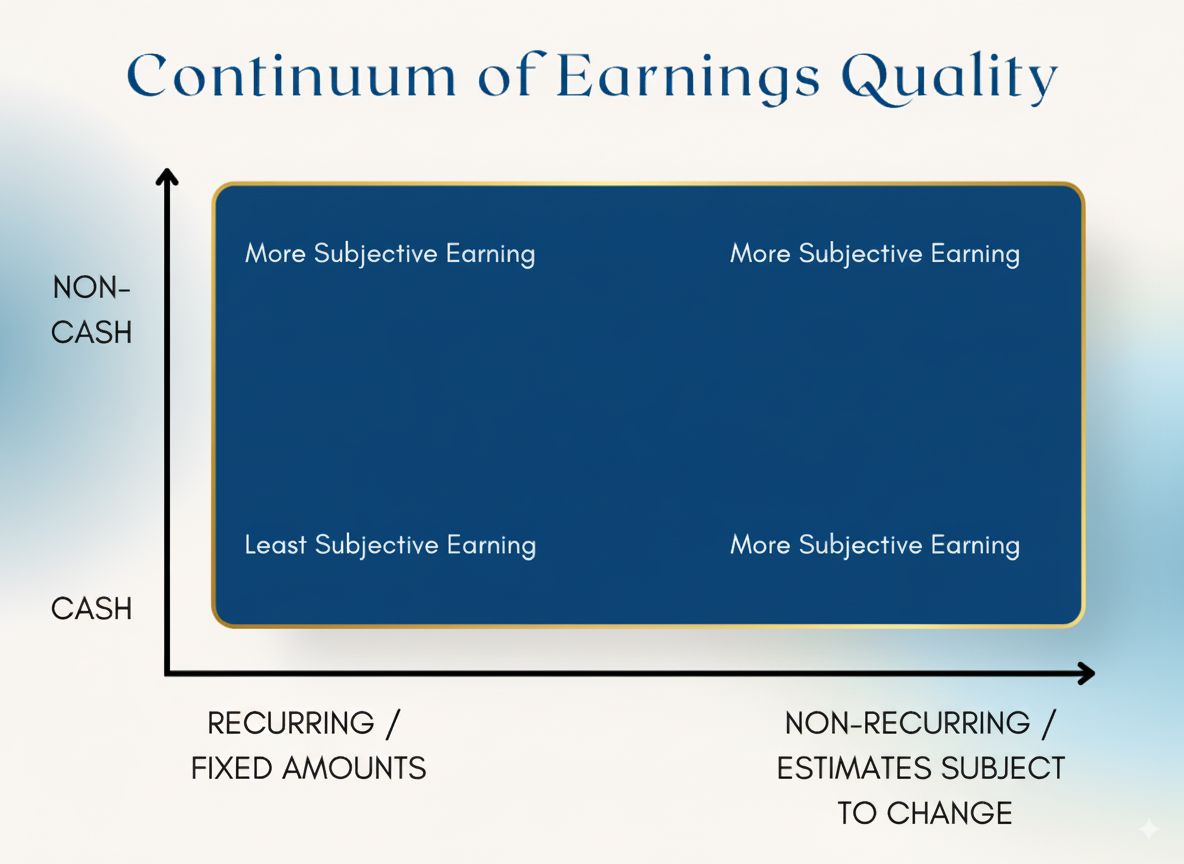
Unlike standard financial statements, a QoE report provides a more transparent view of a company’s true financial performance, stripping away anomalies and one-time events that might skew the picture.
QoE vs Audit: Understanding the Difference
While both QoE reports and traditional audits examine financial data, they serve different purposes:
- QoE Reports: focus on the sustainability and economic nature of earnings, often adjusting for non-operational activities to present a more realistic financial picture.
- Audits: primarily check for compliance with accounting standards (such as GAAP) and provide assurance on the overall accuracy of financial statements.
QoE reports are particularly valuable during M&A transactions, where understanding the true earning potential of a target company is critical. For more insights on investment advisory services, visit Investment Advisory Firm PE VC.
Comprehensive QoE Checklist
A thorough quality of earnings (QoE) checklist typically includes the following key areas:
- Adjusted EBITDA Analysis
- Identify and remove non-recurring items
- Normalize for owner’s compensation and related party transactions
- Revenue and Margin Trends
- Analyze historical revenue growth
- Examine gross and operating margin trends
- Customer and Product Concentration
- Assess reliance on key customers or products
- Evaluate customer retention rates
- Working Capital Analysis
- Review accounts receivable and payable trends
- Analyze inventory turnover and obsolescence
- Accounting Policy Review
- Examine revenue recognition practices
- Assess capitalization policies
- Identification of Unusual or Non-recurring Items
- Isolate one-time gains or losses
- Identify extraordinary expenses or income
- Balance Sheet and Income Statement Normalization
- Adjust for non-operational assets or liabilities
- Normalize for cyclical or seasonal fluctuations
- Tax Exposures
- Review tax compliance history
- Identify potential tax risks or opportunities
- Assessment of Internal Controls and Financial Reporting
- Evaluate the robustness of financial systems
- Assess the quality of management reporting
Each item on this checklist plays a crucial role in uncovering potential financial risks and ensuring the accuracy of reported earnings, ultimately helping buyers or investors make well-informed decisions. For a detailed commercial due diligence checklist, refer to Commercial Due Diligence Checklist Guide.
Key Components of a QoE Report
EBITDA Normalization
EBITDA normalization is a critical process in QoE analysis. It involves adjusting reported EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) for non-recurring items. For guidance on creating effective financial templates, check out Investment Memo Template Guide and Private Equity Deal Sourcing Services Guide.
FAQ
What is the primary purpose of a Quality of Earnings (QoE) report?
The primary purpose of a QoE report is to verify the sustainability and accuracy of a company’s reported earnings by adjusting for non-recurring items, scrutinizing financial projections, assessing revenue recognition practices, and evaluating accounting policies.
How does a QoE report differ from a traditional audit?
While both QoE reports and traditional audits examine financial data, QoE reports focus on the sustainability and economic nature of earnings, often adjusting for non-operational activities. In contrast, traditional audits primarily check for compliance with accounting standards and provide assurance on the overall accuracy of financial statements.
Why is EBITDA normalization important in QoE analysis?
EBITDA normalization is important because it adjusts reported EBITDA for non-recurring items, providing a more accurate picture of a company’s operational performance and helping stakeholders make informed investment decisions.
“`
